Research Article - Der Pharma Chemica ( 2018) Volume 10, Issue 10
Solvent-Free Synthesis and Antimicrobial Potential of Some (2E)-4-methoxyphenyl Chalcones
Thirunarayanan G1* and Vijayakumar S2
1Department of Chemistry, Annamalai University, Annamalainagar 608 002, India
2PG and Research Department of Chemistry, Government Arts College, C-Mutlur, Chidambaram 608 102, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Thirunarayanan G
Department of Chemistry
Annamalai University
Annamalainagar 608 002, India
Abstract
About nine 4-methoxyphenyl enones were synthesized by microwave assisted Crossed-Aldol condensation of 4-methoxyacetophenone and substituted benzaldehydes in the presence of FeCl3/Bentonite catalyst under microwave irradiation. These enones were characterized by melting points, micro analysis and spectroscopic data. The antimicrobial potential of these enones was tested by Bauer-Kirby disc diffusion method. Many of the 4-methoxyphenyl enones shows antimicrobial potential against their microbes.
Keywords
Substituted styryl 4-methoxyphenyl ketones, FeCl3/bentonite catalyst, Biological activities
Introduction
Chalcone possess carbonyl as well as C=C parts in their structure and are called as enones or α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Chalcones have been isolated from artificially and natural process. Chalcones are key intermediates for carbon building blocks. These analogs compounds possess numerous characters by which they find many applications in different fields such as drugs [1-5]. Large number of synthetic routes available for synthesis of α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, the best route is the Crossed-Aldol condensation of equimolar quantities carbonyl substrates with substituted benzaldehydes in base catalysts [6]. Alcoholic base catalysts [7-11] were utilized for carryout the Claisen–Schmidt and Aldol reaction and they produced better yields of a α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. At present large number of catalysts were employed for the synthesis of enones such as anhydrous zinc chloride [10,11] clay minerals [12] ground chemistry catalysts-grinding the carbonyl compounds with base [13], aqueous basic solution in cooling [14], bamboo based sulphonic acids [15], barium hydroxide [16], anhydrous sodium bicarbonate [17], fly-ash: Water, microwave irradiation [10,11,18] and sulphated titania [19]. Kamalakkannan and his co-workers [20] reported the synthesis and evaluation of biological activities of (E)-3-phenyl-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) enones. Recently, the study of green synthetic route and antimicrobial activities of 3-chloro-4-nitrophenyl and phenanthrene enones was reported by Usha et al., [21,22]. The review of literature reflected the little information about the solvent-free synthesis, infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic and evaluation of biological activities study of 2E-4-methoxyphenyl-2-preopen-1-ones. Then the researchers have interested for investigating the greener synthesis and biological activities of 2E-4-methoxyphenyl-2-preopen-1-ones.
Materials and Methods
General
Chemicals used in this work were procured form Sigma-Aldrich and E-Merck chemical companies. Melting points of all 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones were found in Mettler FP51 melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. The UV absorption maxima (λmax, nm) of all 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones were measured in ELICO BL 222 ultraviolet spectrophotometer. The FT IR of all 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones was recorded AVATAR-300 Fourier transform spectrophotometer. Bruker AV400 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer was utilized for measuring the proton and carbon chemical shifts of all 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones in CDCl3 solvent and TMS as internal standard. The micro analyses of the all enones were performed in Thermofennigan CHN analyzer.
Synthesis of chalcones
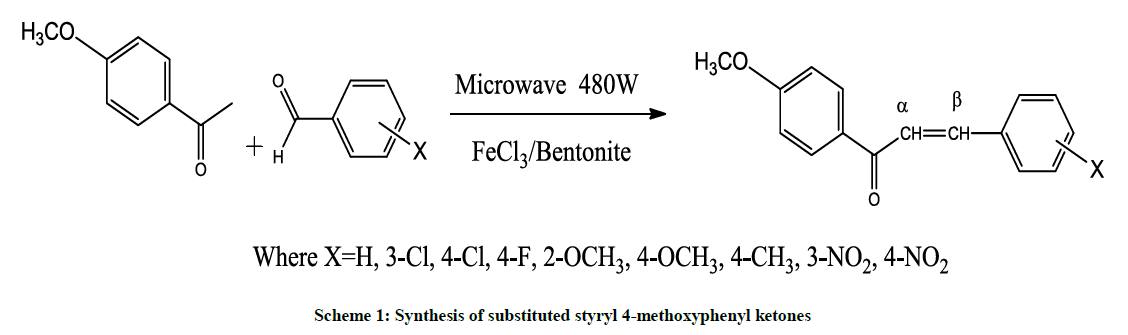
An equal molar quantities of 4-methoxyacetophenone (0.01 mol) with substituted benzaldehydes (0.01 mol) and FeCl3-Bentonite [23] (0.4 g) catalyst were placed in a Borosil beaker and covered with watch glass. The reaction mixture have been irradiated to microwave for 5–6 minutes (Scheme 1) (IFB Microwave Oven, 480 W) and then wait for this mixture attain to room temperature (30ºC). The extraction of organic layer with dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) and evaporation of solvent afforded the crude product. The insoluble catalyst was recycled by purified with ethyl ethanoate and heated in an hot air oven at 100ºC for 1 h. Recrystallization of crude product with benzene-hexane mixture to afforded pale yellow glittering solids. The yield, physical properties and micro analysis data of synthesized 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones are tabulated in Table 1. The characteristic spectroscopic data of all 4-methoxyphenyl chalcones were presented in Table 2.
| Entry | X | M.F. | M.W. | Yield (%) | M. P.(°C) | Micro analysis (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | ||||||
| Found (Calcd.) | Found (Calcd.) | Found (Calcd.) | ||||||
| 1 | H | C16H14O2 | 238 | 90 | 107-108 (108-10) [24] | --- | --- | --- |
| 2 | 3-Cl | C16H13O2 Cl | 272 | 93 | 90-91 | 70.47 -70.46 | 4.76 -4.8 | --- |
| 3 | 4-Cl | C16H13O2Cl | 272 | 94 | 130-131 (130-131) [25] | --- | --- | --- |
| 4 | 4-F | C16H13O2F | 256 | 92 | 110-111 | 75.03 -74.99 | 5.04 -5.11 | --- |
| 5 | 2-OCH3 | C17H16O3 | 268 | 90 | 90-91 | 76.07 -76.1 | 5.98 -6.01 | --- |
| 6 | 4-OCH3 | C17H16O3 | 268 | 92 | 92-93 (100)[25], (93-94) [26] | --- | --- | --- |
| 7 | 4-CH3 | C17H16O2 | 252 | 91 | 134-135 | 80.97 -80.93 | 6.32 -6.39 | --- |
| 8 | 3-NO2 | C16H13O4N | 283 | 91 | 136-137 | 67.86 -67.84 | 4.58 -4.63 | 4.89 -4.94 |
| 9 | 4-NO2 | C16H13O4N | 283 | 92 | 76-77 | 67.82 -67.84 | 4.6 -4.63 | 4.92 -4.94 |
Table 1: The physical constants and analytical data of styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones
| Entry | X | λmax | CO(s-cis) | CO(s-trans) | CHip | CHop | CH=CHop | C=Cop | Hα | Hβ | Cα | Cβ | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | 311.6 | 1653.59 | 1602.95 | 1183.46 | 762.05 | 1018.79 | 561.67 | 7.553 | 7.809 | 121.91 | 144.02 | 188.78 |
| 2 | 3-Cl | 296 | 1664.44 | 1599.02 | 1168.57 | 777.69 | 1018.69 | 560.45 | 7.544 | 7.728 | 123.09 | 142.26 | 188.31 |
| 3 | 4-Cl | 314 | 1652 | 1592 | 1184.65 | 820 | 1017.89 | 560.56 | 7.519 | 7.748 | 122.3 | 142.5 | 188.44 |
| 4 | 4-F | 255 | 1654.78 | 1601.96 | 1185.28 | 821.89 | 1015.85 | 534.15 | 7.477 | 7.768 | 121.58 | 142.7 | 188.53 |
| 5 | 2-OCH3 | 343 | 1655.08 | 1595.18 | 1167.17 | 818.27 | 1016.27 | 528.19 | 7.602 | 7.78 | 119.58 | 143.85 | 188.82 |
| 6 | 4- OCH3 | 346 | 1653.91 | 1595.64 | 1168.67 | 818.98 | 1019.7 | 529.51 | 7.436 | 7.783 | 119.55 | 143.87 | 188.92 |
| 7 | 4-CH3 | 310.8 | 1648.48 | 1593.28 | 1170.2 | 812.82 | 1012.53 | 534.25 | 7.513 | 7.79 | 120.86 | 144.12 | 188.89 |
| 8 | 3-NO2 | 277.5 | 1663.82 | 1599.01 | 1170.96 | 868.75 | 1019.55 | 569.86 | 7.676 | 7.831 | 122.21 | 140.87 | 188.13 |
| 9 | 4-NO2 | 287 | 1668.28 | 1597.17 | 1175.59 | 832.75 | 1033.37 | 570.02 | 7.553 | 7.809 | 123.81 | 146.54 | 195.12 |
Table 2: The Uv-visible absorption maxima (λmax, nm), infrared absorptions (ν, cm-1) and NMR chemical shifts (δ, ppm) of substituted styryl-4- methoxyphenyl ketones
Antimicrobial activities
Measurement of antibacterial sensitivity assay
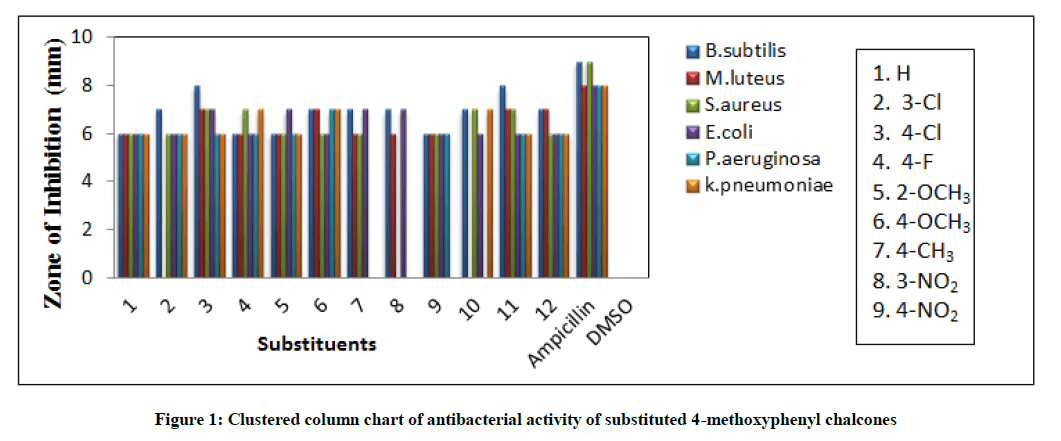
Kirby-Bauer [27] disc diffusion technique was employed for measuring the antibacterial potential of all enones using each three of gram positive microbes namely Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram negative bacterial strains such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia (Table 3). Performing the experiment based on standard disc diffusion method [28-32] using Solidified Mueller Hinton agar on 5 mm diameter of Whatmann No.1 filter paper. Speeded over the 0.5 ml of the test bacterial sample uniformly on the paper, maintained the temperature by incubated for 24 h at 37oC and prevent the water droplets over the medium. The zones of mm of inhibition were measured after 24 h. The measured mm of zone of inhibition values are presented in Table 3.
| Entry | X | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram positive Bacteria | Gram negative Bacteria | ||||||
| Bacillus subtilis | Micrococcus luteus | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Klebsiella pneumoniae | ||
| 1 | H | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 3-Cl | 5 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| 3 | 4-Cl | 6 | --- | 6 | --- | 8 | 7 |
| 4 | 4-F | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 5 | 2-OCH3 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| 6 | 4-OCH3 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 7 | 4-CH3 | 8 | --- | --- | 6 | 6 | --- |
| 8 | 3-NO2 | 7 | --- | 6 | --- | 5 | 6 |
| 9 | 4-NO2 | 6 | --- | 6 | --- | 6 | 7 |
| Standard: Ampicillin | 9 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | |
| Control:DMSO | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | |
Table 3: Anti-bacterial activity of styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones
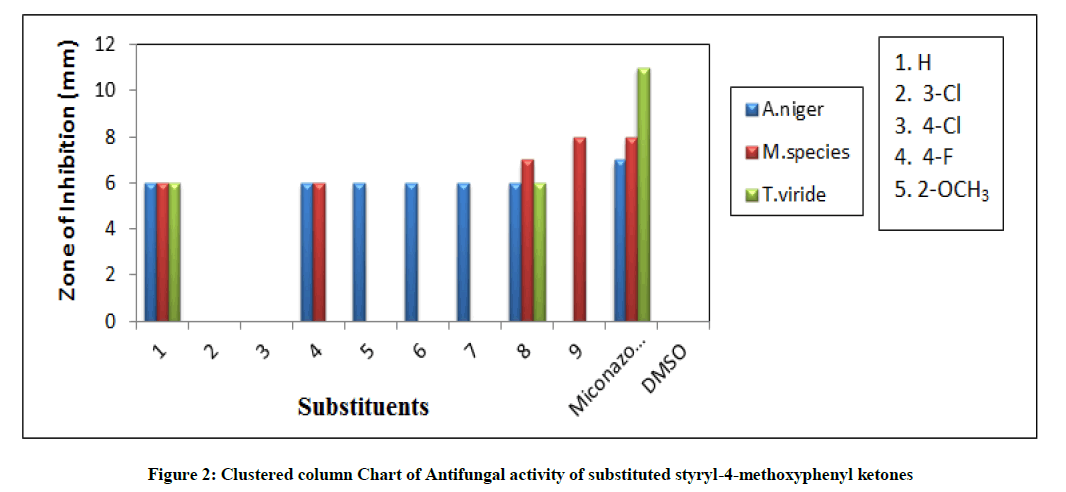
Kirby-Bauer [27] disc diffusion technique was employed for measuring the antifungal potential of all ketones. The standard procedures were used and performed the measurement of mm of zones of inhibition of all compounds with PDA medium and the DMSO as a solvent [28-32]. In this experiment, there are three fungal strains were used namely, Aspergillus niger, Mucor species and Tricoderma viride. The measured mm of zone of inhibition values are tabulated in Table 4.
| Entry | X | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus niger | Mucor species | Tricoderma viride | ||
| 1 | H | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 3-Cl | --- | --- | --- |
| 3 | 4-Cl | --- | --- | --- |
| 4 | 4-F | 6 | 6 | --- |
| 5 | 2-OCH3 | 6 | --- | --- |
| 6 | 4-OCH3 | 6 | --- | --- |
| 7 | 4-CH3 | 6 | --- | --- |
| 8 | 3-NO2 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 9 | 4-NO2 | --- | 8 | --- |
| Standard | Miconazole | 7 | 8 | 11 |
| Control | DMSO | --- | --- | --- |
Table 4: Antifungal activity of substituted styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones
Results and Discussion
Antibacterial activity
The measured antibacterial potential of substituted styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones were tabulated in Table 3. The statistical comparison diagram was illustrated in Figure 1. Styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones having the substituents 4-Cl, 4-F, -OCH3, CH3 and 3-NO2 showed good antibacterial activities against B. subtilis stain. The H, 3-Cl and 4-NO2 substituted styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones showed satisfactory activities against B. subtilis stain. Here punctual operation of the +I and –I effects of the substituents gave good and satisfactory antibacterial activity. Good antibacterial activities were observed for the ketones possess the substituents H, 3-Cl, 4-F and -OCH3 against M. luteus stain. The 4-Cl, 4-CH3, 3-NO2 and 4-NO2 substituted ketones not showed antibacterial activity against M. luteus stain.
Here the inductive and hyper conjugative effects of substituents were failed for showing antibacterial activity. All chalcones except 4-CH3 substituent showed good antibacterial activity against S. aureus strain. Here the hyper conjugative effect of methyl group was absent for showing antibacterial activity against S. aureus strain. The ketones have H, 3-Cl, 4-F, -OCH3 and CH3 substituent shows good antibacterial activity against E. coli. The remaining 4-Cl, 3-NO2 and 4-NO2 substituted ketones have no antibacterial activity against E. coli. Here the inductive effect of the substituents was complete absent. All ketones show good antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa. The 3-NO2 substituted ketones showed satisfactory antibacterial activity. All styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones show good antibacterial activity against K. pneumonia stain except CH3 substituent. Here the inductive effect of the methyl group was completely absent for giving the antibacterial activity.
Antifungal activity
The measured antifungal activities of substituted styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones were tabulated in Table 4. The statistical comparison diagram was illustrated in Figure 2. The ketones having substituents H, 4-F, -OCH3, CH3 and 3-NO2 showed good antifungal activity against A. niger fungal microbes. The 4-Cl and 4-NO2 substituted ketones have no antifungal activity against A. niger stain. Here the +I effect of the chloro and nitro substituents were completely absent for producing the fungal activity. The parent (H), 4-F and 3-NO2 substituted chalcones showed good antifungal activity against Mucor species. The ketones have 3-Cl, -OCH3 and CH3 substituted chalcones have not shown the antifungal activity against Mucor species. This is due to the +I, -I and resonance-conjugative effects of these substituents were failing for giving the antifungal activity against Mucor species. The H (parent) and 3-NO2 substituted ketones have shown satisfactory antifungal activity against Tricoderma viride fungal microbe. The -Cl, -F, -OCH3, -CH3 and 4-NO2 substituted ketones have not shown fungal activity against T. viride fungal stain. The failure for showing the antifungal activity was due to the absence of inductive, resonance and hyper conjugative effects of the substituents.
Conclusion
The authors have demonstrated the simple greener Crossed-Aldol condensation for synthesis of styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones using FeCl3/Bentonite catalyst. In this investigation, the authors observed more than 90% yields. These styryl ketones were characterized by melting points, micro analysis and spectroscopic data. The Bauer-Kirby disc diffusion method was utilized for finding the antimicrobial activities. Styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones having the substituents 4-Cl, 4-F, -OCH3, CH3 and 3-NO2 showed good antibacterial activities against B. subtilis stain. Good antibacterial activities were observed for the ketones possess the substituents H, 3-Cl, 4-F and -OCH3 against M. luteus stain. All chalcones except 4-CH3 substituent showed good antibacterial activity against S. aureus strain. The ketones have H, 3-Cl, 4-F, -OCH3 and CH3 substituent shows good antibacterial activity against E. coli. All ketones show good antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa. All styryl-4-methoxyphenyl ketones show good antibacterial activity against K. pneumonia strain except CH3 substituent. The ketones having substituents H, 4-F, -OCH3, CH3 and 3-NO2 showed good antifungal activity against A. niger fungal microbes. The parent (H), 4-F and 3-NO2 substituted chalcones showed good antifungal activity against Mucor species. The H (parent) and 3-NO2 substituted ketones have shown satisfactory antifungal activity against T. viride fungal microbe.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank DST NMR facility, Department of Chemistry, Annamalai University, Annamalainagar-608 002, for recording NMR spectra of all compounds.
References
- C.L. Mirinda, G.L. Aponso, J.F. Stevens, M.L. Denizer, D.R. Buhler, Cancer Lett., 2000, 149, 21.
- K. Monostory, V. Tamasi, L. Vereckey, P. Perjesi, Toxicol., 2003, 184, 203.
- Z. Nowakowska, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2007, 42, 125.
- R.R.T. Majinda, B.M. Abegaz, M. Bezabih, B.T. Ngadjui, C.C.W. Wanjala, L.L. Mdee, G. Bojase, A. Sialyo, I. Masesane, S.O. Yeboah, Pure Appl. Chem., 2001, 73, 1197.
- M. Sitaram Kumar, J. Das, J. Iqbal, S. Trehan, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2007, 42, 538.
- G. Thirunarayanan, P. Ananthakrishna Nadar, A. J. Chem., 2002, 14, 1518.
- G. Venkat Reddy, D. Maitraie, B. Narsaiah, R. Rambabu, P.S. Rao, Synth. Commun., 2001, 31(18), 2881.
- G. Thirunarayanan, P. Ananthakrishna Nadar, J. Korean Chem. Soc., 2006, 50, 183.
- G. Thirunarayanan, P. Ananthakrishna Nadar, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 2006, 83, 1107.
- G. Thirunarayanan, Indian J. Chem., 2007, 46B, 1511.
- G. Thirunarayanan, J. Korean Chem. Soc., 2007, 51, 115.
- R. Ballini, G. Bosica, R. Maggi, M. Ricciutelli, P. Righi, G. Sartori, R. Sartorio, Green Chem., 2001, 3, 178.
- G. Thirunarayanan, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 2008, 84, 447.
- S.A. Basaif, T.R. Sobahi, A.K. Khalil, M.A. Hassan, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2005, 26 (11), 1677.
- Q. Xu, Z. Yang, D. Yin, F. Zhang, Catal. Commun., 2008, 9 (1), 1579.
- H.E. Blackwell, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2006, 10 (3), 203.
- Z. Zhang, Y.W. Dong, G.W. Wang, Chem. Lett., 2003, 32 (10), 966.
- G. Thirunarayanan, P. Mayavel, K. Thirumurthy, Spectrochim. Acta., 2012, 91A, 18.
- B. Krishnakumar, R. Velmurugan, M. Swaminathan, Catal. Commun., 2011, 12 (5), 375.
- D. Kamalakkannan, G. Vanangamudi, G. Thirunarayanan, Der Pharma Chemica., 2017, 9(12), 34.
- V. Usha, V. Thangaraj, G. Thirunarayanan, Indian J. Chem.,2017, 56B, 1094.
- V. Usha, V. thangaraj, G. Thirunarayanan, Org. Prep. Int. Proc., 2018.
- I. Muthuvel, S. Dineshkumar, K. Thirumurthy, B. Krishnakumar, G. Thirunarayanan, Indian J. Chem., 2016, 55B, 252.
- S. Syam, S.I. Abdelwahab, M.A. Al-Mamary, S. Mohan, Molecules., 2012, 17, 6179.
- D. Kakati, J.C. Sarma, Chem. Central. J.,2011, 5(8), 2.
- M.G. Ahmed, U.K.R. Romman, S.M. Ahmed, M.D.K. Akhter, M.D.E. Halim, Ban. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2007, 42(1), 45.
- A.W. Bauer, W.M. Kirby, J.C. Sherris, M. Truck, Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 1966, 45, 493.
- G. Vanangamudi, R. Sundararajan, R. Arulkumaran, S. Vijayakumar, G. Thirunarayanan, Der Pharma Chemica., 2013, 5(6), 213.
- G. Thirunarayanan and G. Vanangamudi, Arabian J. Chem., 2014, 7, 1055.
- G. Vanangamudi, M. Subramanian, P. Jayanthi, R. Arulkumaran, D. Kamalakkannan, G. Thirunarayanan, Arabian J. Chem., 2016, 9, S717.
- G. Thirunarayanan and K. G. Sekar, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2016, 20, 661.
- R. Arulkumaran, R. Sundararajan, S. Vijayakumar, S. P. Sakthinathan, R. Suresh, D. Kamalakkannan, K. Ranganathan, G. Vanangamudi, G. Thirunarayanan, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 20, 2016, S122.