Research Article - Der Pharma Chemica ( 2018) Volume 10, Issue 4
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Chalcones of 3-Benzylidene-2-chlorocyclohex-1-enecarbaldehyde as Potential Anti-proliferative Agents
Kathiravan PR1,2*, Muthukumaran S2, Dhatchanamoorthy N1, Prince AAM2 and Venugopal M3
1Orchid Pharma Limited, Plot Nos, 138-149, SIDCO Industrial Estate, Alathur, Thiruporur, Kanchipuram District- 603110, Tamil Nadu, India
2Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda College, Department of Chemistry, Mylapore, Chennai-600004, India
3Ven Biotech Private Limited, Chennai, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Kathiravan PR
Orchid Pharma Limited
Plot Nos, 138-149, SIDCO Industrial Estate, Alathur
Thiruporur, Kanchipuram District- 603110, Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract
A series of novel chalcones of 3-Benzylidene-2-chlorocyclohex-1-enecarbaldehyde were synthesized by reacting benzylidene derivative of chloro aldehyde with different aromatic and heterocyclic ketones. All the synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR and Mass spectra. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro cytotoxicity. In particular, the compounds of the series 5 and fluorinated compounds of 5-9 exhibited superior cytotoxic property.
Keywords
Vilsmeier reaction, Chalcones, Benzylidene derivatives of chloro aldehyde, Cytotoxicity
Introduction
Chalcones are biosynthesized in a variety of plants as a precursor to flavonoids and isoflavonoids. Chemically, chalcones are 1,3-diphenyl-2- propen-1-ones, where the two aromatic rings are connected by a α, β unsaturated system comprising of three carbon atoms. The trans form is thermodynamically favourable among the cis and trans isomeric forms of chalcones [1]. Chalcones being an exceptional chemical template bears variety of pharmacological activities [2-4] which include antimalarial [5], antitubercular [6], antioxidant [7], anti-inflammatory [8,9], anti- HIV [10], antiviral [11], hepatoprotective activities [12] and aldose reductase inhibitory activities [13]. The functional groups attached to the aryl rings greatly influence the biological activities displayed by chalcones whereas the partial or full removal of α, β unsaturated ketone pharmacophore results in loss of bioactivity. In comparison to clinically prevailing and proven anticancer drugs, chalcones were found to possess lesser side effects and have tendency to interact with amino groups of nucleic acid [14]. Sofalcone is a synthetic analogue of sophoradin used as anti-ulcer agent [15].
In continuation of studies on the chemistry of chalcones and their biological importance in anti-cancer properties, we synthesized novel chalcones from chloro aldehydes of benzylidene through aldol condensation followed by Vilsmeier reaction to obtain benzylidene derivatives chloro aldehydes. The resulting chloro aldehyde derivatives were reacted with aromatic and heterocyclic ketones namely acetophenone, 2- methoxyacetophenone, 2-acetylfuran, 2-acetylthiophene and 2-acetyl pyridine in ethanol, water and a base to give the expected chalcones.
Materials and Methods
All chemicals and reagents used were of laboratory grade and procured from Sigma Aldrich. All solvents used were purchased from commercial suppliers. Melting points were determined using a Buchi apparatus by open capillary tube method and are uncorrected. IR spectra were recorded using a PerkinElmer series 2000 Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrophotometer from KBr pellets. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Advance 400 spectrometer. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm relative to Tetramethylsilane (TMS) as internal standard. Coupling constants (J) are in hertz (Hz). Proton and carbon spectra were typically obtained at room temperature. Mass spectra were recorded on an Perkin Elmer Sciex API 3000 ESI mass spectrometer. Precoated silica gel GF254 plates from Merck were used for thin-layer chromatography. Elemental analyses were carried out using a Thermo Finnigan Flash EA 1112 elemental analyzer.
Synthesis of 2-benzylidenecyclohexanone derivatives (3a-d)
The compounds were synthesized according to previously reported procedure [16,17].
Synthesis of 3-benzylidene-2-chlorocyclohex-1-enecarbaldehyde derivatives (4a-d)
The compounds were synthesized according to previously reported procedure [18].
General procedure for synthesis of compounds 4a-d
To dimethylformamide (45 ml), phosphorous oxychloride (0.12 mol) was added drop wise over a period of 15-30 min with stirring at 0-5°C. Compound 3a-d (0.05 mol) dissolved in Dimethylformamide (DMF, 70 ml) was added drop wise, followed by warming to room temperature, heating to temperature of 55-60°C maintained for 4 h, cooling, and pouring slowly into 50% solution of sodium acetate in water (100 ml) at 0- 5°C. The product was filtered, washed with water, followed by slurry washing with ethanol (100 ml) to afforded compounds 4a-d.
General procedure for synthesis of compounds 5a-d, 6a-d, 7a-d, 8a-d & 9a-d [19]
A compounds 4a-d (0.01 mol), was reacted with respective aryl and heterocyclic ketone (0.01 mol) and potassium hydroxide (0.012 mol) in ethanol (40 ml) and water (1 ml) was stirred at 25-30°C for 1-2 h. The reaction was monitored by TLC (Hexane: ethyl acetate (9:1). After the reaction was completed, the product was filtered, washed with ethanol, afforded corresponding chalcones.
The structure of the synthesized compound was confirmed by spectral data (IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and Mass) and elemental analyses. As a characteristic sample, IR spectrum of the compound (5d) revealed that the band at around 1650 cm-1 corresponds to the carbonyl group of the ketone group. In the 1H-NMR spectra, the singlets at δ 7.22 ppm correspond to benzylidene proton of the cyclohexyl moiety. The singlets at δ=2.33 ppm correspond to methyl protons. The multiplet at around δ=2.79-2.76, 2.72-2.69 and 1.78-1.72 ppm correspond to the methylene protons of cyclohexyl group. The 13C-NMR spectrum recorded in DMSO-d6 showed a signal at δ=189.6 ppm, corresponding to carbonyl carbon of the ketone group. The signals at 28.3 ppm, 27.4 ppm and 21.7 ppm confirmed the methylene carbons of cyclohexyl group. The signal at 21.3 ppm corresponds to methyl carbon. Mass spectrum acquired in positive ionization ESI mode, showed a signal at 349.1 Da corresponds to [M + H]+, confirmed the molecular mass of the compound. All these experimental data unambiguously confirmed the structure of the compound 5d.
3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-phenyl-propenone (5a): Yellow powder; yield: 68%; m.p. 160-162°C; IR (KBr) cm-1: 2950, 1651, 1561, 1293, 1014, 774 cm-1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.15-8.10 (m, 3H), 7.69-7.66 (m, 1H), 7.59-7.56 (m, 2H), 7.47-7.42 (m, 5H), 7.34-7.30 (m, 1H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 2.79-2.77 (m, 2H), 2.73-2.70 (m, 2H), 1.79-1.72 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.7, 141.1, 137.9, 137.8, 136.7, 135.2, 134.1, 133.7, 131.1, 130.0, 129.3, 128.9, 128.8, 128.1, 124.8, 28.2, 27.4, 21.7; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 334.1; found: 335.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C22H19ClO (%): C, 78.91; H, 5.72; found (%): C, 78.95; H, 5.76.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-fluoro-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-phenyl-propenone (5b): Orange powder; yield: 73%; m.p. 158-160°C; IR (KBr) cm-1: 2937, 1654, 1563, 1293, 1019, 768 cm-1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.14-8.10 (m, 3H), 7.70-7.66 (m, 1H), 7.59-7.56 (m, 2H), 7.46-7.42 (m, 2H), 7.44 (s, 1H), 7.28-7.25 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 2.77-2.66 (m, 4H), 1.79-1.73 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.7, 163.1, 160.6, 141.1, 137.9, 137.7, 135.1, 134.1, 133.7, 133.2, 133.1, 132.1, 132.1, 130.0, 129.3, 128.9, 124.8, 115.9, 115.7, 28.7, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 352.1; found: 353.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C22H18ClFO (%): C, 74.89; H, 5.14; found (%): C, 74.87; H, 5.16.
3-[3-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-phenyl-propenone (5c): Brown powder; yield: 70%; m.p. 148-150°C; IR (KBr) cm- 1: 2938, 1655, 1566, 1297, 1015, 771 cm-1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.13-8.09 (m, 3H), 7.70-7.64 (m, 1H), 7.62-7.56 (m, 4H), 7.51- 7.44 (m, 1H), 7.39-7.37 (m, 2H), 7.23 (s, 1H), 2.76-2.69 (m, 4H), 1.79-1.74 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.7, 141.0, 137.9, 137.6, 135.9, 134.6, 133.8, 132.1, 131.8, 129.9, 129.3, 128.9, 125.0, 121.4, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 412.0; found: 413.0 [M + H]+, 415.0 [M + H]2+; anal. calcd. for C22H18BrClO (%): C, 63.87; H, 4.39; found (%): C, 63.89; H, 4.43.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-methyl-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-phenyl-propenone (5d): Orange powder; yield: 72%; m.p. 128-130°C; IR (KBr) cm-1: 2937, 1650, 1566, 1294, 1016, 774 cm-1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.15-8.10 (m, 3H), 7.70-7.66 (m, 1H), 7.59-7.56 (m, 2H), 7.46-7.42 (m, 1H), 7.33-7.31 (m, 2H), 7.24 (m, 2H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 2.79-2.76 (m, 2H), 2.72-2.69 (m, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.78-1.72 (m, 2H); 13CNMR (100MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.6, 141.2, 138.1, 138.0, 137.7, 134.5, 133.9, 133.7, 131.2, 130.0, 129.5, 129.3, 128.9, 124.5, 28.3, 27.4, 21.7, 21.3; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 348.1; found: 349.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C23H21ClO (%): C, 79.18; H, 6.07; found (%): C, 79.22; H, 6.11.
3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-propenone (6a): Yellow powder; yield: 69%; m.p. 108-110 °C; IR (KBr) cm-1: 2948, 1650, 1567, 1294, 1034, 783 cm-1; 1H-NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.14-8.10 (m, 1H), 7.72 (d, J = 7.64 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (bs, 1H), 7.51-7.47 (m, 1H), 7.46-7.41 (m, 5H), 7.35-7.30 (m, 1H), 7.28-7.24 (m, 2H), 3.85 9 (s, 3H), 2.79-2.69 (m, 4H), 1.78-1.73 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.4, 160.0, 141.2, 139.4, 137.9, 136.7, 135.2, 134.1, 131.2, 130.5, 130.0, 128.9, 128.2, 124.9, 121.5, 119.8, 113.4, 55.9, 28.2, 27.4, 21.7; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 364.1; found: 365.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C23H21ClO2 (%): C, 75.71; H, 5.80; found (%): C, 75.75; H, 5.78.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-fluoro-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-propenone (6b) Yellow powder; yield: 75%; m.p. 128-130°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2941, 1649, 1558, 1299, 782 cm-1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.13-8.09 (m, 1H), 7.72 (d, J=7.64 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (bs, 1H), 7.51-7.45 (m, 4H), 7.41 (s, 1H), 7.27-7.23 (m, 4H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.76-2.69 (m, 4H), 1.78-1.74 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.4, 163.1, 160.6, 160.0, 141.1, 139.4, 137.7, 135.2, 134.2, 133.2, 133.1, 132.2, 132.1, 130.5, 130.0, 124.9, 121.5, 119.8, 115.9, 115.7, 113.4, 55.9, 28.1, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 382.1; found: 383.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C23H20ClFO2 (%): C, 72.15; H, 5.27; found (%): C, 72.19; H, 5.29.
3-[3-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-propenone (6c): Yellow powder; yield: 72%; m.p. 122- 124°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2936, 1649, 1562, 1300, 1027, 783 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.13-8.09 (m, 1H), 7.72 (d, J=7.56 Hz, 1H), 7.62-7.59 (m, 2H), 7.56 (bs, 1H), 7.52-7.46 (m, 2H), 7.43-7.37 (m, 2H), 7.27-7.22 (m, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.75-2.69 (m, 4H), 1.77-1.74 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.4, 160.0, 141.1, 139.4, 137.6, 135.9, 134.6, 132.1, 131.8, 130.5, 129.9, 125.1, 121.5, 1211.4, 119.8, 113.4, 55.9, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 442.0; found: 443.0 [M + H]+, 445.0 [M + H]2+; anal. calcd. for C23H20BrClO2 (%): C, 62.25; H, 4.54; found (%): C, 62.27; H, 4.56.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-methyl-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-propenone (6d): Yellow powder; yield: 77%; m.p. 124- 126°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2939, 1650, 1557, 1300, 1027, 785 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.14-8.10 (m, 1), 7.72 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (bs, 1H), 7.51-7.47 (m, 1H), 7.43-7.39 (m, 1H), 7.33-7.31 (m, 2H), 7.24-7.22 (m, 4H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.77-2.70 (m, 4H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.75 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.4, 160.0, 141.3, 139.5, 138.1, 137.8, 134.5, 133.9, 133.7, 131.3, 130.5, 130.0, 129.5, 124.6, 121.5, 119.7, 113.4, 55.9, 28.3, 27.4, 21.7, 21.3; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 378.1; found: 379.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C24H23ClO2 (%): C, 76.08; H, 6.12; found (%): C, 76.12; H, 6.14.
3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-furan-2-yl-propenone (7a): Yellow powder; yield: 72%; m.p. 152-153°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2956, 2864, 1642, 1578, 1462, 1050, 871, 753 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.13 (s, 1H), 8.08-8.07 (m, 1H), 7.78 (d, J=3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (m, 1H), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.35-7.32 (m, 1H), 7.28-7.27 (m,, 2H), 7.23 (m, 1H), 6.80-6.79 (m, 1H), 2.79-2.77 (m, 2H), 2.68-2.66 (m, 2H), 1.77- 1.74 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=175.0, 153.4, 149.0, 139.9, 137.8, 136.7, 135.2, 133.8, 131.2, 130.0, 128.9, 128.2, 124.6, 120.1, 113.3, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 324.1; found: 325.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C20H17ClO2 (%): C, 73.96; H, 5.28; found (%): C, 73.94; H, 5.26.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-fluoro-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-furan-2-yl-propenone (7b): Yellow powder; yield: 72%; m.p. 142-144 °C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2934, 2861, 1647, 1569, 1465, 1044, 882, 764 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.12-8.08 (m, 2H), 7.78-7.77 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.49-7.46 (m, 2H), 7.27-7.23 (m, 4H), 6.79-6.78 (m, 1H), 2.76-2.74 (m, 2H), 2.68-2.65 (m, 2H), 1.77-1.74 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 176.9, 153.4, 149.0, 139.9, 137.7, 135.1, 133.9, 133.2, 133.1, 132.2, 132.1, 130.0, 124.6, 120.1, 115.9, 115.7, 113.3, 28.1, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 342.1; found: 343.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C20H16ClFO2 (%): C, 70.08; H, 4.70; found (%): C, 70.12; H, 4.72.
3-[3-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-furan-2-yl-propenone (7c): Yellow powder; yield: 77%; m.p. 154-156°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2956, 2877, 1645, 1568, 1463, 1052, 845, 766 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.11-8.08 (m, 2H), 7.78-7.77 (d, J=3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.62-7.57 (m, 2H), 7.39-7.36 (m, 2H), 7.27-7.20 (m, 2H), 6.79-6.78 (m, 1H), 2.76-2.73 (m, 2H), 2.68-2.65 (m, 2H), 1.78-1.72 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=176.9, 153.4, 149.1, 139.9, 137.6, 136.0, 135.9, 134.3, 132.1, 131.8, 129.9, 124.8, 121.4, 120.2, 113.3, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 402.0; found: 403.0 [M + H]+, 405.0 [M + H]2+; anal. calcd. for C20H16BrClO2 (%): C, 59.50; H, 3.99; found (%): C, 59.54; H, 4.02.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-methyl-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-furan-2-yl-propenone (7d): Yellow powder; yield: 77%; m.p. 160-162°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2943, 2858, 1641, 1562, 1466, 1047, 848, 794 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.13-8.07 (m, 2H), 7.77-7.76 (d, J=3.5 Hz, 1H), 7.32-7.30 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.24-7.21 (m, 4H), 6.79-6.78 (m, 1H), 2.78-2.75 (m, 2H), 2.67-2.64 (m, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.78-1.72 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=176.9, 153.4, 148.9, 140.0, 138.1, 13.7, 134.5, 133.9, 133.4, 131.3, 130.0, 129.5, 124.4, 120.0, 113.3, 28.3, 27.4, 21.6, 21.3; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 338.1; found: 339.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C21H19ClO2 (%): C, 74.44; H, 5.65; found (%): C, 74.46; H, 5.67.
3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-pyridin-3-yl-propenone (8a): Yellow powder; yield: 74%; m.p. 148-151°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2946, 2869, 1656, 1561, 1319, 1031, 874, 790 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.80-8.79 (m, 1H), 8.23-8.22 (m, 1H), 8.12-8.04 (m, 2H), 7.92-7.88 (m, 1H), 7.73-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.44-7.42 (m, 4H), 7.35-7.31 (m, 2H), 2.80-2.78 (m, 2H), 2.69-2.66 (m, 2H), 1.79-1.76 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ-189.1, 153.8, 149.7, 141.1, 138.3, 135.3, 133.9, 131.5, 130.0, 128.9, 128.2, 123.0, 28.2, 27.5, 21.8; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 335.1; found: 336.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C21H18ClNO (%): C, 75.11; H, 5.40; N, 4.17; found (%): C, 75.09; H, 5.42; N, 4.19.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-fluoro-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-pyridin-3-yl-propenone (8b): Yellow powder; yield: 78%; m.p. 150-152°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2946, 2869, 1657, 1561, 1320, 1032, 875, 791 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.80-8.79 (m, 1H), 8.25-8.21 (m, 1H), 8.12-8.04 (m, 2H), 7.92-7.88 (m, 1H), 7.72-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.49-7.46 (m, 2H), 7.37-7.28 (m, 2H), 7.27-7.23 (m, 1H), 2.77-2.74 (m, 2H), 2.68-2.65 (m, 2H), 1.78-1.75 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.1, 153.7, 149.7, 141.0, 138.3, 138.2, 15.2, 134.0, 133.8, 133.2, 132.2, 132.1, 130.3, 129.2, 129.1, 128.2, 123.4, 123.0, 115.9, 115.7, 28.1, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 353.1; found: 354.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C21H17ClFNO (%): C, 71.29; H, 4.84; N, 5.37; found (%): C, 71.31; H, 4.86; N, 5.39.
3-[3-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-pyridin-3-yl-propenone (8c): Brown powder; yield: 73%; m.p. 166-168°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2952, 2880, 1663, 1567, 1318, 1025, 885, 791 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.80-8.79 (m, 1H), 8.24-8.20 (m, 1H), 8.12-8.06 (m, 2H), 7.93-7.89 (m, 1H), 7.72-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.64-7.60 (m, 2H), 7.39-7.38 (m, 2H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 2.75-2.74 (m, 2H), 2.68-2.65 (m, 2H), 1.78-1.75 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=189.1, 153.7, 140.9, 138.3, 138.2, 135.9, 134.4, 132.1, 131.8, 130.1, 128.2, 123.6, 123.0, 28.1, 27.5, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 413.0; found: 414.0 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C21H17BrClNO (%): C, 60.82; H, 4.13; N, 3.38; found (%): C, 60.86; H, 4.11; N, 3.40.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-methyl-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-pyridin-3-yl-propenone (8d): Yellow powder; yield: 70%; m.p. 148-150°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2949, 2883, 1664, 1577, 1317, 1025, 882, 792 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.79-8.78 (m, 1H), 8.25-8.21 (m, 1H), 8.11-8.04 (m, 2H), 7.91-7.87 (m, 1H), 7.72-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.34-7.32 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (m, 1H), 7.24-7.23 (m, 2H), 2.79-2.77 (m, 2H), 2.67- 2.64 (m, 2H), 1.79-1.73 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=188.1, 153.3, 149.2, 140.6, 138.2, 137.8, 137.3, 134.0, 133.4, 133.1, 131.1, 129.6, 128.9, 127.7, 122.7, 122.5, 27.7, 26.9, 21.2, 20.8; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 349.1; found: 350.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C22H20ClNO (%): C, 75.53; H, 5.76; N, 4.00; found (%): C, 75.57; H, 5.80; N, 4.02.
3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-thiophen-2-yl-propenone (9a): Yellow powder; yield: 82%; m.p. 158-160°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2948, 2866, 1636, 1577, 1412, 1233, 1048, 757 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.27-8.27 (m, 1H), 8.12-8.07 (m, 2H), 7.43-7.42 (m, 2H), 7.34-7.33 (m, 1H), 7.32-7.31 (m, 2H), 7.28 (m, 1H), 7.25-7.22 (m, 2H), 2.79-2.77 (m, 2H), 2.72-2.69 (m, 2H), 1.78-1.75 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=181.9, 145.8, 140.3, 137.8, 136.3, 135.2, 134.6, 134.3, 133.9, 131.2, 130.0, 129.6, 129.4, 124.7, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 340.0; found: 341.0 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C20H17ClOS (%): C, 70.47; H, 5.03; found (%): C, 70.49; H, 5.05.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-fluoro-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-thiophen-2-yl-propenone (9b): Yellow powder; yield: 70%; m.p. 142-144°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2926, 2864, 1633, 1562, 1412, 1221, 1061, 827 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.27-8.25 (m, 1H), 8.11-8.06 (m, 2H), 7.48-7.44 (m, 2H), 7.41-7.37 (m, 1H), 7.32-7.28 (m, 1H), 7.26-7.22 (m, 3H), 2.76-2.73 (m, 2H), 2.70-2.67 (m, 2H), 1.78-1.72 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=181.9, 163.1, 160.6, 145.8, 140.3, 137.7, 136.2, 135.1, 135.0, 134.2, 133.9, 133.2, 133.1, 132.1, 132.0, 130.0, 129.4, 124.7, 115.9, 115.7, 28.1, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 358.1; found: 359.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C20H16ClFOS (%): C, 66.94; H, 4.49; found (%): C, 66.98; H, 4.47.
3-[3-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-thiophen-2-yl-propenone (9c): Brownish yellow powder; yield: 72%; m.p. 140- 142°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2927, 2862, 1637, 1569, 1412, 1221, 1060, 828 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.27-8.25 (m, 1H), 8.10-8.07 (m, 2H), 7.61-7.59 (d, J=8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.42-7.36 (m, 3H), 7.32-7.29 (m, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 2.75-2.73 (m, 2H), 2.71-2.68 (m, 2H), 1.79-1.73 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=181.9, 145.8, 140.2, 137.6, 136.3, 136.0, 135.9, 134.4, 134.3, 132.0, 131.8, 129.8, 129.4, 124.9, 121.4, 28.2, 27.4, 21.6; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 418.0; found: 419.0 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C20H16BrClOS (%): C, 57.23; H, 3.84; found (%): C, 57.27; H, 3.86.
3-[2-Chloro-3-(4-methyl-benzylidene)-cyclohex-1-enyl]-1-thiophen-2-yl-propenone (9d): Yellow powder; yield: 70%; m.p. 130-132°C; IR (KBr) cm−1: 2932, 2864, 1635, 1568, 1412, 1230, 1056, 797 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=8.27-8.26 (m, 1H), 8.122-8.06 (m, 2H), 7.39-7.36 (m, 1H), 7.33-7.28 (m, 3H), 7.24-7.22 (m, 3H), 2.79-2.76 (m, 2H), 2.70-2.67 (m, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.78-1.72 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=181.9, 145.8, 140.4, 138.1, 137.7, 136.2, 134.5, 134.2, 133.9, 133.6, 131.3, 130.0, 129.5, 129.4, 124.4, 28.3, 27.4, 21.6, 21.3; ESI-MS m/z calcd. 354.1; found: 355.1 [M + H]+; anal. calcd. for C21H19ClOS (%): C, 71.07; H, 5.40; found (%): C, 71.09; H, 5.42.
Biology
Anticancer activity (Cytotoxicity assay)
Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cell Line (HCT116) and non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line (NCI-H460) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. They were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, GIBCO-Thermo), 100 units/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (GIBCO-Thermo) at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. Cells were seeded at 3 × 103 cells/well in 96-well plates and growth inhibition assays were performed in the presence of different drug concentrations ranging from 20 μM to 0.01 μM. After 48 h, at the end of the incubation, a Sulphorhodamine-B (SRB) assay [20] was performed to determine the cellular growth and viability.
Results and Discussion
Chemistry
In the present work, we have synthesized series of novel chalcone from benzylidene derivatives chloro aldehydes (Scheme 1). Initially, cyclohexanone was condensed with aldehydes in the presence of sodium hydroxide in water at 90-95°C through a reported procedure to get 3a-d [16,17]. The above condensation products were subjected to Vilsmeier reaction using Dimethylformamide (DMF) & phosphorous oxychloride (POCl3) to yield chloro aldehydes 4a-d in 60-70% yield [18].
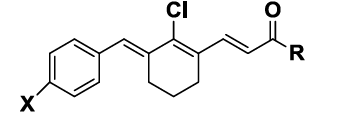
In preparation of chalcone derivatives of chloro aldehyde, compound 4a-d is reacted with various aryl and heterocyclic ketone derivatives {RCOCH3 (R = Phenyl, 2-methoxy phenyl, Furan, Pyridine, Thiophene)} in the presence of potassium hydroxide in aqueous ethanol at 25-30 °C for 1-2 h afforded the chalcones (5a-d, 6a-d, 7a-d, 8a-d & 9a-d) in 65-80% yield. [19]. The compounds were confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR and Mass spectra.
Biological Evaluation
Anticancer activity
The synthesised compounds 5a-d, 6a-d, 7a-d, 8a-d & 9a-d were evaluated for their anti-proliferative property against two cancer cell lines namely, the colon cancer HCT116 cancer cell line and lung cancer NCI-H460 cell line. The in vitro anticancer activities of the members of the series 5-9 were expressed in GI50 values, which are presented in Table 1. The natural chalcone Curcumin was taken as reference drug. Compounds (Chalcones) of this series contain halogen or methyl substituted phenyl ring on one end and aryl/heterocyclic ring on another end. Among series 5-9, the best activity profile was displayed by compounds with aryl ring of series 5 whereas the compounds of series 6 and 9 were essentially inactive (GI50 > 15 μM). Each compound of the series 5 except 5c were found to exhibit cytotoxic activity comparable to curcumin in HCT116 cell line. Among the different substituents (F, Br and methyl) to phenyl ring, the fluorine substitution was advantageous for cytotoxic property irrespective of the nature of aryl/heterocyclic ring. In the case of furan substituted benzylidene chalcones, halogen or methyl substitution to the aryl ring (7b-d) greatly enhanced the cytotoxic property which was otherwise inactive (7a). On the other hand, phenyl substitution was well tolerated whereas 2-methoxy phenyl or heterocyclic (furan, thiophene or pyridine) substituted chalcones were less cytotoxic. In contrary to the general notion that methoxy substitution to the aryl ring of chalcone favour anticancer property, 2-methoxy phenyl substituted aryl chalcone in our study was inactive. This indicated that cytotoxicity is likely to be modulated by the position of methoxy substitution on the phenyl ring. Thus, our preliminary cytotoxic data identified novel benzylidine chalcones as a potential antiproliferative agent for cancer therapy.
 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Compounds | X | R | GI50 (µM) | |
| HCT116 | NCI-H460 | ||||
| 5 | 25 | ||||
| 2 | 5b | F | Phenyl | 6 | 15 |
| 3 | 5c | Br | Phenyl | 25 | 45 |
| 4 | 5d | CH3 | Phenyl | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 6a | H | 2-methoxy Phenyl | 18 | 22 |
| 6 | 6b | F | 2-methoxy Phenyl | 10 | 15 |
| 7 | 6d | Br | 2-methoxy Phenyl | >100 | >100 |
| 8 | 6d | CH3 | 2-methoxy Phenyl | 100 | >100 |
| 9 | 7a | H | Furan | >100 | >100 |
| 10 | 7b | F | Furan | 4.5 | 6 |
| 11 | 7c | Br | Furan | 6 | 10 |
| 12 | 7d | CH3 | Furan | 7 | 11 |
| 13 | 8a | H | Pyridine | 20 | 20 |
| 0 | 8b | F | Pyridine | 20 | 6 |
| 15 | 8c | Br | Pyridine | 20 | 20 |
| 16 | 8d | CH3 | Pyridine | 4 | 4 |
| 17 | 9a | H | Thiophene | 28 | 45 |
| 18 | 9b | F | Thiophene | 12 | 30 |
| 19 | 9c | Br | Thiophene | 35 | >100 |
| 20 | 9d | CH3 | Thiophene | 20 | 45 |
| 21 | Curcumin | 2.6 | 7.6 | ||
Table 1: In vitro anticancer activity for the compounds 5a-d, 6a-d, 7a-d, 8a-d & 9a-d
Conclusion
In summary, a new series of novel chalcones of 3-Benzylidene-2-chlorocyclohex-1-enecarbaldehyde (5-9) were synthesized and characterized by using 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR and Mass spectra. The synthesized compounds were screened for their in vitro cytotoxicity. The derivatives of 3-(3-Benzylidene-2-chloro-cyclohex-1-enyl)-1-phenylpropenone 5a-d showed promising anti-proliferative activity against human colon cancer cell line HCT116 and lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. In general, the fluorine substituted benzylidine chalcones were found to possess more cytotoxic activity in comparison to other substituents (bromine or methyl) to the phenyl ring. Overall, our results highlight the cytotoxic property of synthesised benzylidene chalcones and on the nature of the substituents on the aryl/phenyl ring determining the cytotoxic potential.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the management of Orchid Pharma Limited, Chennai-600119, India and Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda College, Chennai-600004, India for providing the required facilities.
References
- D.I. Batovska, I.T. Todorova, Curr. Clin. Pharmocol., 2010,5, 1.
- N.K. Sahu, S.S. Balbhadra, J. Choudhary, D.V. Kohil, Curr. Med. Chem., 2012, 19, 209.
- L. Ni, C.Q. Meng, J.A. Sikorski, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat.,2004, 14, 1669.
- M. Bijo, J. Suresh, S. Anbazghagan, J. Paulraj, G.K. Krishnan, Biomedicine & Preventive Nutrition.,2014, 4, 451.
- J.N. Dominguez, J.E. Charris, G. Lobo, D.N. De Domminguze, M.M. Moreno, F. Riggione, E. Sanchez, J. Olson, P.J. Rosenthal, Eur. J. Med. Chem.,2001, 36, 555.
- L.D. Chiaradia, A. Mascarello, M. Purificacao, J. Vernal, M.N. Cordeiro, M.E. Zenteno, A. Villarino, R.J. Nunes, R.A. Yunes, H. Terenzi, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2008, 18, 6227.
- C.L. Miranda, J.F. Stevens, V. Ivanov, M. Mccall, B. Frei, M.L. Deinzer, J. Agric. Food. Chem.,2000, 48, 3876.
- J. Wu, J. Li, Y. Cai, Y. Pan, F. Ye, Y. Zhang, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 8110.
- Z.A. Nowakowska, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2007, 42, 125.
- J.H. Wu, X.H. Wang, Y.H. Yi, K.H. Lee, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2003, 13, 1813.
- J.S. Biradar, B.S. Sasidhar, R. Parveen, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 4074.
- O. Sabzevari, S. Mahmoudian, B. Minaei, H. Paydar, Toxicol. Lett., 2010, 196, 213.
- M. Chlupacova, V. Opletalova, Chem. Listy., 2004, 98, 320.
- H.J. Zhang, Y. Qian, D.D. Zhu, X.G. Yang, H.L. Zhu, Eur. J. Med. Chem.,2011, 46, 4702.
- Mark Bamford, Prog. Med. Chem., 2009, 47, 75.
- K. Kawazoe, Y. Yoshida, U.S. Patent-2010, 780856
- H. Vieweg, G. Wagner, Pharmazie., 1979, 34, 785.
- P.R. Kathiravan, M. Venugopal, S. Muthukumaran, Res. Chem. Intermed.,2017, 44, 2315.
- T.P. Selvam, V. Karthick, P.V. Kumar, M.A. Ali, Drug Discov. Ther.,2012, 6, 198.
- A. De Vasconcelos, V.F. Campos, F.K. Nedel Seixas, O.A. Dellagostin, K.R. Smith, C.M. De Pereira, F.M. Stefanello, T. Collares, A.G. Barschak, Cell Biochem. Funct., 2013, 31, 289.